Cardiovascular disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, affecting millions of people annually. It encompasses a range of heart and blood vessel conditions that can severely impact a person's quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for cardiovascular disease is crucial for early detection and management.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of cardiovascular disease, including its risk factors, prevention strategies, and the latest advancements in treatment. By educating yourself about this condition, you can take proactive steps toward maintaining heart health.
Whether you're concerned about your own cardiovascular health or that of a loved one, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and resources needed to make informed decisions. Let's delve into the world of cardiovascular disease and explore how we can combat this global health challenge.
Read also:Runelite Mobile The Ultimate Guide To Enhancing Your Old School Runescape Experience
Table of Contents
- What is Cardiovascular Disease?
- Common Types of Cardiovascular Disease
- Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
- Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
- Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease
- Treatment Options for Cardiovascular Disease
- Prevention Strategies for Cardiovascular Disease
- Lifestyle Changes to Improve Heart Health
- Global Statistics on Cardiovascular Disease
- Future Research Directions in Cardiovascular Disease
What is Cardiovascular Disease?
Cardiovascular disease refers to a group of disorders that affect the heart and blood vessels. These conditions can lead to serious health complications, including heart attacks and strokes. The most common forms of cardiovascular disease involve the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels, which can disrupt blood flow to vital organs.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases are responsible for approximately 17.9 million deaths each year, making them the leading cause of mortality globally. This highlights the urgent need for increased awareness and preventive measures.
While some forms of cardiovascular disease are congenital, many develop over time due to lifestyle choices and underlying health conditions. Understanding the nature of these diseases is the first step toward effective management.
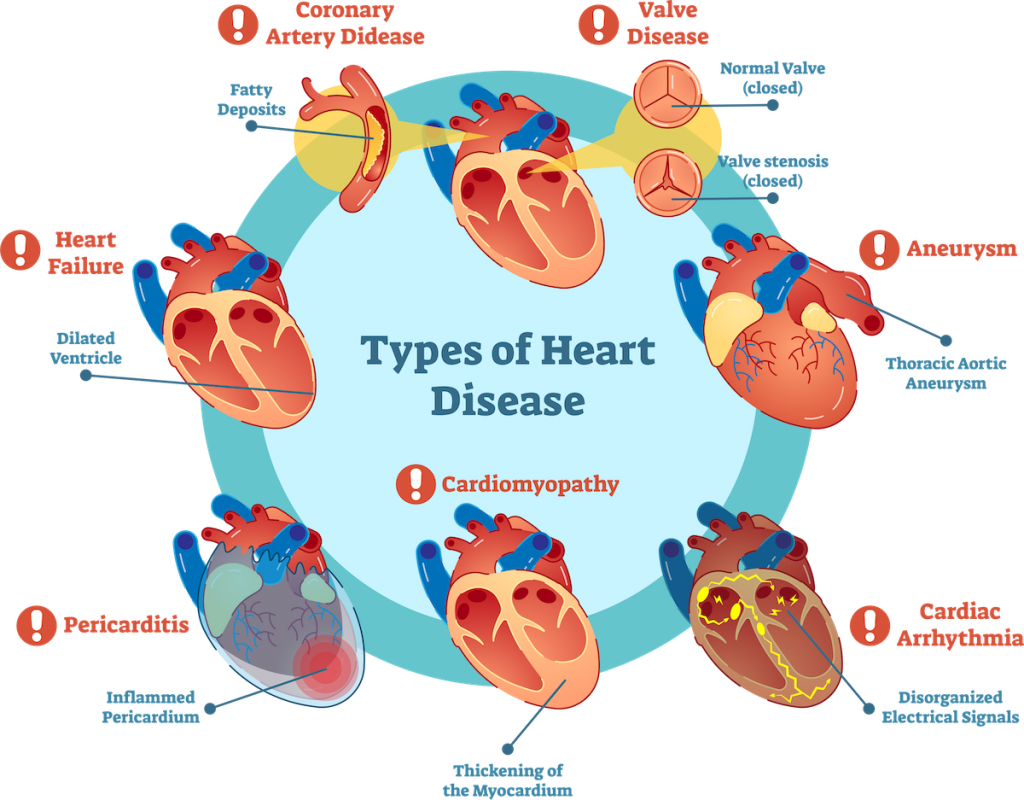
Common Types of Cardiovascular Disease
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most prevalent type of cardiovascular disease. It occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque. This condition can lead to chest pain (angina) and heart attacks.
Heart Failure
Heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. This can result in fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing this condition.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Strokes can cause permanent brain damage and are a major cause of disability worldwide.
Read also:Teacutea Leoni Height A Comprehensive Guide To Her Career And Life
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
Several risk factors contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. These include both modifiable and non-modifiable factors:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Diabetes
- Family history of heart disease
- Age and gender
Identifying and addressing these risk factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
The symptoms of cardiovascular disease can vary depending on the specific condition. Some common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
It's important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as early intervention can prevent severe complications.
Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease
Diagnosing cardiovascular disease involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Common tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Stress test
- Coronary angiography
- Blood tests
These tests help healthcare providers assess the condition of the heart and blood vessels, enabling them to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Cardiovascular Disease
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing cardiovascular disease. Commonly prescribed drugs include:
- Statins for lowering cholesterol
- Antiplatelet agents to prevent blood clots
- Beta-blockers to reduce heart rate and blood pressure
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to treat cardiovascular disease. These include:
- Angioplasty and stenting
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- Valve repair or replacement
Advancements in medical technology have improved the success rates of these procedures, offering hope to patients with severe cardiovascular conditions.
Prevention Strategies for Cardiovascular Disease
Preventing cardiovascular disease involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and managing risk factors. Key strategies include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Avoiding tobacco use
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
By incorporating these practices into daily life, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Heart Health
Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting a heart-healthy diet is one of the most effective ways to prevent cardiovascular disease. Focus on consuming:
- Lean proteins
- Low-fat dairy products
- Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids
Regular Exercise
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week can strengthen the heart and improve circulation. Activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming are excellent choices.
Global Statistics on Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease remains a significant public health issue worldwide. Key statistics include:
- Approximately 17.9 million people die from cardiovascular diseases each year
- Ischemic heart disease and stroke account for two-thirds of all cardiovascular-related deaths
- Low- and middle-income countries bear the greatest burden of cardiovascular disease
These figures underscore the importance of global efforts to combat cardiovascular disease through education, policy changes, and improved healthcare access.
Future Research Directions in Cardiovascular Disease
Ongoing research in the field of cardiovascular disease aims to uncover new treatments and prevention strategies. Areas of focus include:
- Genetic factors contributing to cardiovascular risk
- Development of personalized medicine approaches
- Investigation of novel drug therapies
As science continues to advance, the hope is that these efforts will lead to breakthroughs in managing and ultimately eradicating cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular disease is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this life-threatening illness.
We encourage readers to share this article with friends and family, promoting awareness and education about cardiovascular health. For further information, explore additional resources on our website or consult with a healthcare professional.